
Current pandemic trends bring more uncertainty to economic prospects
16 December 2021

VIENNA, 16 December 2021 - The most recent data on global manufacturing production, corresponding to the third quarter of 2021, indicate a stabilization after the COVID-19-related economic halt in the previous year. While the economic trajectories vary significantly among countries, most economies experienced solid increases in manufacturing production compared to 2020. Furthermore, higher technology industries had a better production performance and, therefore, recovered faster. However, renewed restrictions to fight another infection wave since November 2021, as well as the appearance of new coronavirus variants, may again threaten the economic recovery and future prosperity.
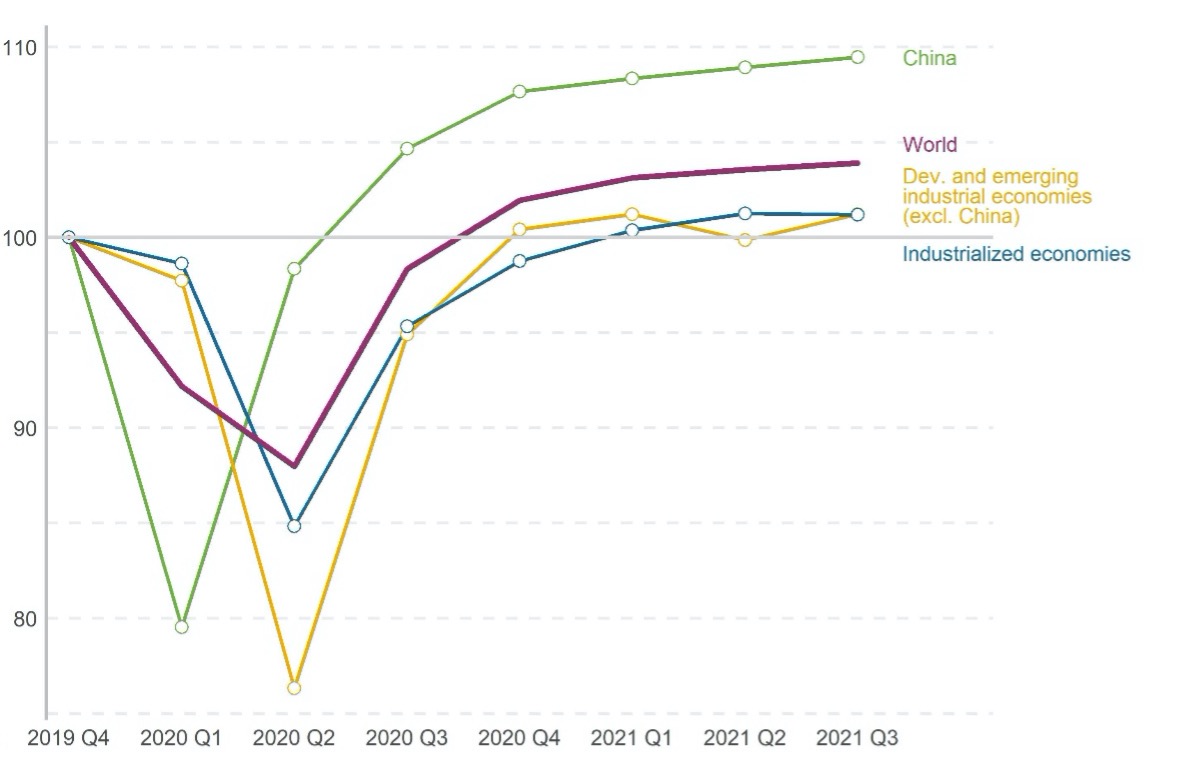
The latest UNIDO World Manufacturing Report, published by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), includes the most recent official data on global manufacturing production and points to a stabilizing year-over-year growth of 5.7 per cent in the third quarter of 2021. However, the report also shows a different pace of recovery across regions. China, for example, quickly bounced back and already exceeded its pre-pandemic production level since the third quarter of 2020. Nevertheless, in the current quarter, China experienced the lowest annual growth rate (4.6 per cent) since 2006, excluding the first two pandemic-related quarters in 2020. Production in developing and emerging industrial economies (Dev. and EIE) has recorded a greater volatility, even falling below pre-pandemic levels in the second quarter of 2021, as the pandemic has affected countries in this group at different periods. Industrialized economies, on the other hand, exceeded their pre-pandemic production level since the first quarter of 2021 and are now facing a stable year-over-year growth of 6.1 per cent.
Figure 1. Index of industrial production (Q4 2019 = 100)

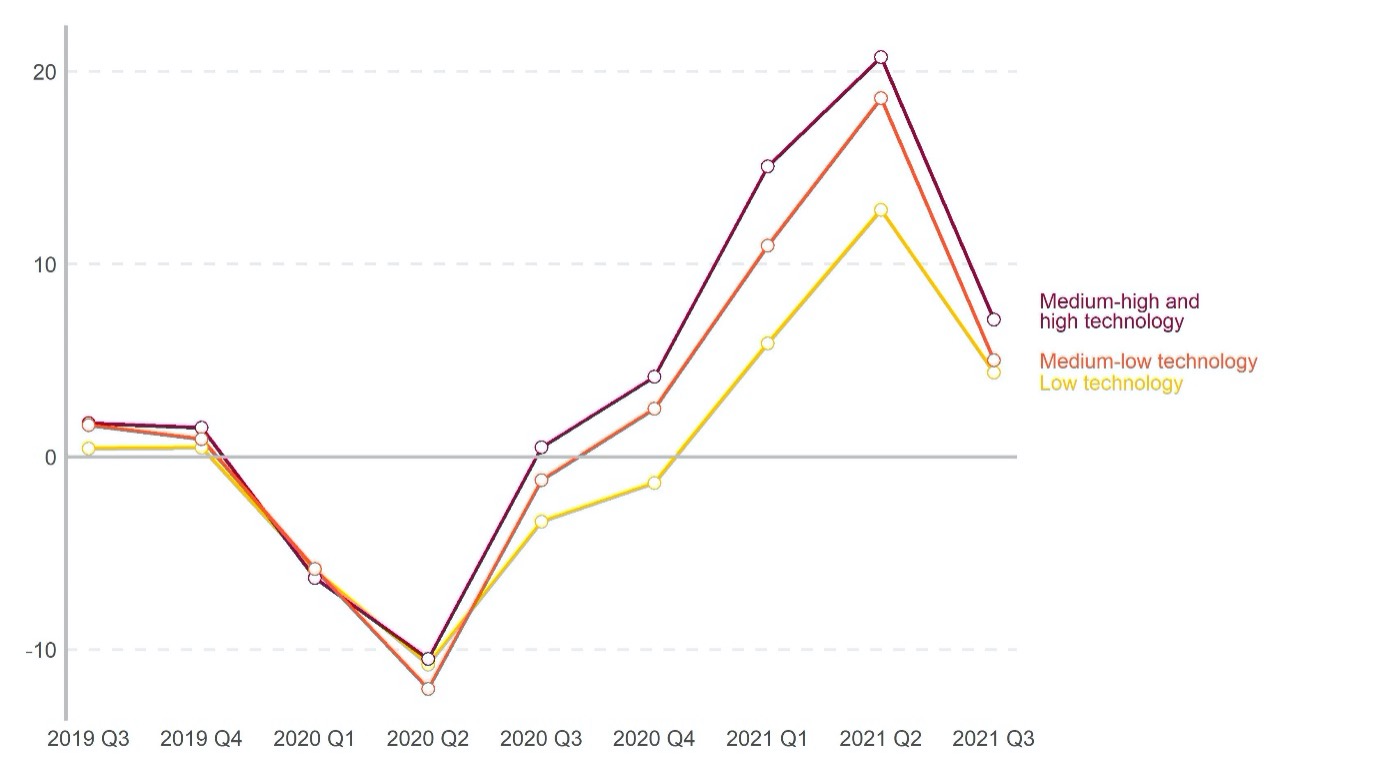
The UNIDO report also reveals varying trends across different industrial sectors. Output of industries using medium-high- and high-technology increased by 7.1 per cent in the third quarter of 2021, while lower technology industries faced slightly lower increases of around four per cent. Many of the higher technological industries already reached and exceeded the pre-pandemic production levels. However, the manufacturing of motor vehicles, for example, was not able to reach production levels prior the pandemic and even faced a year-over-year output reduction of 8.9 per cent due to supply chain difficulties.
Figure 2. Quarterly growth of manufacturing industries by technological intensity, percentage change compared to the same quarter of the previous year
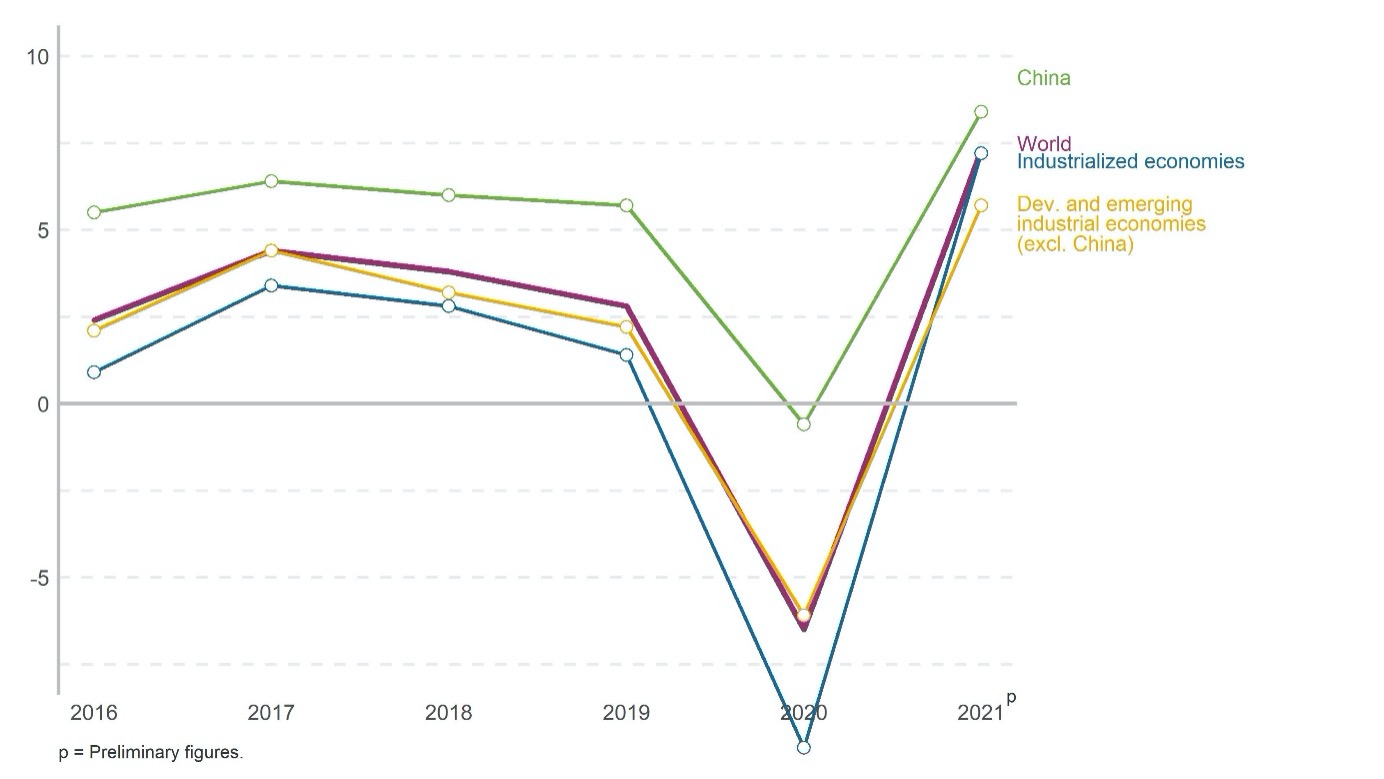
The latest UNIDO forecasts of manufacturing value added (MVA) in 2021, updated in October 2021, point towards a recovery after the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 outbreak and the resulting containment measures around the world. Global manufacturing production is expected to grow by 7.3 per cent in 2021, while China's manufacturing sector will most likely expand its production by 8.4 per cent (after a drop of 0.6 per cent in the previous year). MVA in industrialized economies is estimated to grow by 7.2 per cent in 2021 (compared to a drop of 9.9 per cent in 2020). The manufacturing sector of developing and emerging industrial economies (excl. China) is expected to recover at an even faster pace, bouncing from a drop of 6.1 per cent in 2020 to an increase of 5.7 per cent in 2021.
Figure 3. Annual growth rates in manufacturing value added in constant 2015 US$
The full report is available here. It presents the most recent trends of global manufacturing at country, regional and industry level.
All data and analysis are based on seasonally adjusted data. Data can be downloaded through the UNIDO data portal or consulted in official UNIDO publications. For more information, please contact UNIDO Statistics.